When it comes to autism, assessments play a vital role in the diagnosis and understanding of the condition. An autism assessment is a comprehensive evaluation that aims to identify and evaluate the presence of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in individuals. This process involves a combination of different components and tools to gather information and make an accurate diagnosis.

What is an Autism Assessment?
An autism assessment is a thorough evaluation conducted by professionals who specialize in autism spectrum disorder (ASD). It involves a series of assessments, observations, and interviews to assess an individual’s behavior, communication skills, social interactions, and developmental milestones. The assessment process takes into account the individual’s medical and developmental history, as well as their current functioning.
The goal of an autism assessment is to determine whether an individual meets the criteria for an ASD diagnosis based on established diagnostic criteria, such as the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) or the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-11). By conducting a comprehensive assessment, professionals can gain a deeper understanding of an individual’s strengths, challenges, and specific needs.
Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis of autism is crucial as it allows for early intervention and tailored treatment plans that can significantly improve a child’s developmental outcomes and quality of life. Research has shown that early intervention can lead to positive outcomes in areas such as communication, social skills, and behavior management.
By identifying autism at an early stage, parents and caregivers can access appropriate resources, therapies, and support services that can help their child thrive. Early intervention can also provide families with the necessary tools and strategies to navigate the challenges associated with autism.
It’s important to note that autism assessments should always be conducted by professionals with expertise in autism spectrum disorder (ASD). These professionals consider an individual’s strengths and challenges across various settings and situations, ensuring a comprehensive and accurate evaluation.

Components of an Autism Assessment
To gain a comprehensive understanding of autism, a thorough autism assessment involves several key components. These components include reviewing the individual’s medical and developmental history, conducting direct observation and interviews, and utilizing standardized assessments.
Medical and Developmental History
A crucial aspect of an autism assessment is gathering a detailed medical and developmental history of the individual. This includes information about prenatal and birth history, early development milestones, and any medical conditions or genetic factors that may be relevant. The medical and developmental history provides valuable insights into the individual’s overall health and developmental trajectory.
Direct Observation and Interviews
Direct observation and interviews play a vital role in the assessment process. Professionals trained in autism assessment techniques carefully observe the individual’s behavior, communication skills, social interactions, and play patterns. These observations can take place in various settings, such as home, school, or clinical settings. Interviews with caregivers or family members are also conducted to gather valuable information about the individual’s behavior, strengths, challenges, and developmental history.
Standardized Assessments
Standardized assessments are an essential component of an autism assessment. These assessments utilize validated tools and measures to assess various aspects of the individual’s development, behavior, and communication skills. Professionals administer these assessments to gather objective data and compare the individual’s performance to established norms. Examples of standardized assessments commonly used in autism assessments include the Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule (ADOS) and the Autism Diagnostic Interview-Revised (ADI-R). These assessments provide valuable information for the diagnostic process.
By incorporating these components, an autism assessment aims to provide a comprehensive evaluation of the individual’s strengths, challenges, and developmental profile. This multidimensional approach ensures a thorough understanding of the individual’s unique characteristics and helps in making an accurate autism diagnosis. It is important to note that an autism assessment is a complex and time-intensive process, requiring expertise from professionals in the field of autism spectrum disorder (ASD).

Screening for Co-Occurring Conditions
When it comes to autism assessments, it is not only important to evaluate autism itself but also to screen for co-occurring conditions that may accompany autism. Many individuals with autism may also have other conditions that impact their development and daily functioning. In this section, we will explore the common co-occurring conditions associated with autism and the process of assessing these conditions.
Common Co-Occurring Conditions
Autism often co-occurs with several other conditions that can have a significant impact on an individual’s overall well-being. Some of the common co-occurring conditions include:
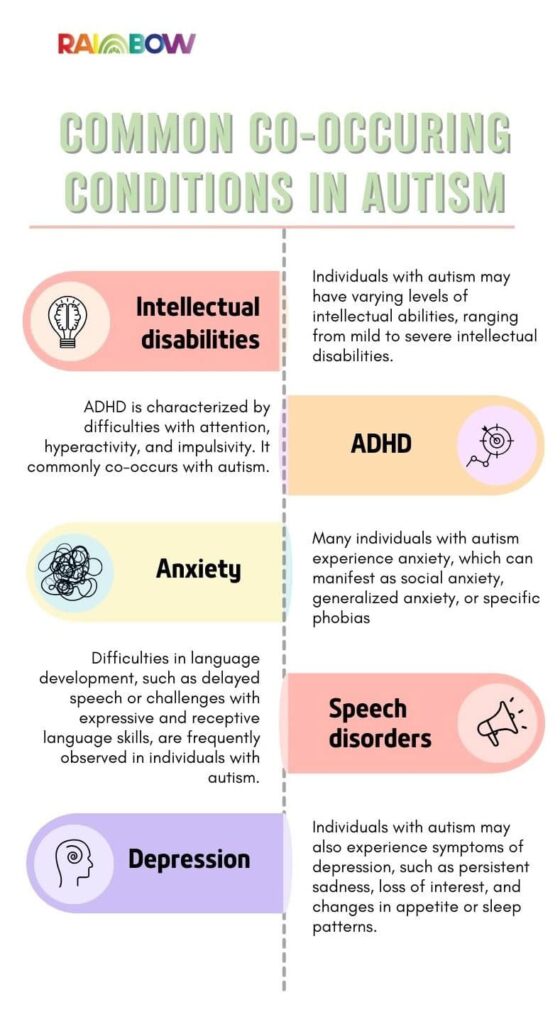
Assessing these co-occurring conditions is crucial for developing a comprehensive understanding of an individual’s needs and providing appropriate support and intervention.
Assessing for Co-Occurring Conditions
During the autism assessment process, professionals will evaluate the presence of co-occurring conditions. This assessment involves gathering information from multiple sources, including parents, caregivers, and teachers or school professionals. The assessment may also include direct observation of the individual and various screening measures for specific conditions.
Professionals conducting the assessment may use a variety of tools and tests to gather information. These may include:
- Autism Diagnostic Interview-Revised (ADI-R): A comprehensive interview that assesses the individual’s developmental history and current behaviors related to autism.
- Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule (ADOS): A standardized observation protocol used to assess social communication, play, and repetitive behaviors associated with autism.
- Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS): A rating scale used to assess the severity of autism symptoms.
- Other assessments: Depending on the specific needs and concerns of the individual, additional assessments may be conducted to evaluate language and communication skills, intellectual abilities, adaptive behaviors, motor skills, and sensory experiences.
By gathering information from various sources and employing appropriate assessment tools, professionals can gain a comprehensive understanding of the individual’s strengths, challenges, and specific needs.
Tools and Tests Used in Autism Assessments
Autism assessments involve a comprehensive evaluation process that incorporates various tools and tests to gather information about a child’s behavior, development, and symptoms. These assessments are conducted by professionals who specialize in diagnosing autism spectrum disorder (ASD). In this section, we will explore some of the commonly used tools and tests in autism assessments, including the Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule (ADOS), the Autism Diagnostic Interview-Revised (ADI-R), and other assessment tools.
Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule (ADOS)
The Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule (ADOS) is a standardized assessment tool widely used in autism assessments. It involves direct observation of the individual’s social interactions, communication, and play skills. The ADOS consists of various structured activities designed to elicit behaviors relevant to the diagnosis of ASD. Trained professionals carefully observe and score the individual’s responses, providing valuable information for the diagnostic process.
Autism Diagnostic Interview-Revised (ADI-R)
The Autism Diagnostic Interview-Revised (ADI-R) is a comprehensive interview conducted with the parents or caregivers of the individual being assessed. The ADI-R covers various aspects of the individual’s developmental history, including early development, language skills, social interactions, and repetitive behaviors. The interview provides valuable insights into the individual’s past and current behaviors, aiding in the diagnostic process.
Other Assessment Tools
In addition to the ADOS and ADI-R, there are other assessment tools commonly used in autism assessments. These tools may vary depending on the specific needs and preferences of the evaluating professional. Some examples of other assessment tools used in autism assessments include:
- Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS): The CARS is a rating scale that assesses the presence and severity of autism symptoms. It involves direct observation of the individual’s behavior and interactions, as well as interviews with parents or caregivers.
- Social Communication Questionnaire (SCQ): The SCQ is a questionnaire completed by parents or caregivers. It assesses the individual’s communication and social interaction skills, providing valuable information for the diagnostic process.
- Developmental and Cognitive Assessments: Children suspected of having autism may undergo various developmental and cognitive assessments to evaluate their specific strengths and challenges. These assessments may include measures of language abilities, cognitive functioning, and adaptive skills.
The specific combination of tools and tests used in an autism assessment may vary depending on the evaluating professional and the needs of the individual being assessed. These assessments are designed to gather comprehensive information from multiple sources, including interviews, observations, and standardized tests. The collaborative efforts of professionals from various disciplines contribute to a thorough understanding of the individual’s strengths, challenges, and potential autism diagnosis.
Professionals Involved in Autism Assessments
When it comes to autism assessments, it is crucial to have professionals with expertise in autism spectrum disorder (ASD) involved in the process. These professionals play a vital role in accurately assessing and diagnosing autism in individuals. Additionally, they take into consideration the individual’s strengths and challenges across various settings and situations.
Expertise in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
Professionals involved in autism assessments have specialized knowledge and experience in working with individuals on the autism spectrum. They may include:
- Developmental Pediatricians: These medical professionals specialize in the development and behavior of children. They play a pivotal role in diagnosing autism and assessing developmental delays.
- Child Psychologists and Psychiatrists: These mental health professionals evaluate the child’s behaviors, emotions, and cognitive abilities. They use various assessment tools and techniques to gather information about the child’s behavior and development.
- Speech-Language Pathologists: These professionals assess the child’s language and communication skills, which are crucial in diagnosing autism. They evaluate the child’s ability to understand and use language and assess any difficulties in social communication.
- Occupational Therapists: These professionals assess the child’s sensory processing, motor skills, and daily living skills. They look for any challenges the child may have in activities of daily living, such as self-care, fine motor skills, and sensory integration.
Considering the expertise of these professionals ensures a comprehensive and accurate assessment of autism, taking into account the various aspects of the individual’s development and behavior.
Considering Strengths and Challenges

Professionals evaluate the child’s behaviors, communication skills, cognitive abilities, and social interactions to determine if they meet the criteria for an autism diagnosis. They take into account the individual’s strengths, such as special interests, unique talents, and areas where they excel. By recognizing and understanding these strengths, professionals can tailor interventions and support services to promote the individual’s growth and development.
At the same time, professionals also assess the challenges the individual may face in areas such as social communication, sensory processing, and adaptive behaviors. By identifying these challenges, appropriate interventions and strategies can be implemented to address and support the individual’s specific needs.
Feedback and Recommendations
Following an autism assessment, it is important for individuals to receive feedback on the results and recommendations for intervention and support services. This feedback plays a crucial role in understanding the assessment outcomes and developing a comprehensive plan to address the specific needs of the individual.
Providing Assessment Results
After completing the assessment process, professionals involved in the evaluation will provide detailed feedback on the assessment results. This feedback typically includes an explanation of the assessment findings, which may involve discussing the child’s strengths and challenges, as well as any areas of concern. The feedback aims to provide a clear understanding of the assessment outcomes and assist parents and caregivers in comprehending the implications for their child.
It is important to note that receiving an autism diagnosis can be an emotional experience for parents and caregivers. Therefore, professionals delivering the assessment results should approach the feedback session with empathy, compassion, and sensitivity. They should be prepared to answer questions, address concerns, and offer support to parents and caregivers during this crucial stage.
Intervention and Support Services
One of the primary goals of the autism assessment is to develop an individualized intervention plan tailored to the needs of the individual. Based on the assessment results, professionals will offer recommendations for intervention and support services that can help address the challenges and promote the overall well-being of the individual.
Intervention and support services may vary depending on the individual’s specific needs and the resources available in their community. These services can include various forms of therapy, such as behavioral therapy, speech and language therapy, occupational therapy, and social skills training. The intervention plan may also involve educational support, counseling, and assistance with accessing community resources.
It is crucial for parents and caregivers to actively engage in the intervention process and collaborate with professionals to ensure that the recommended services are implemented effectively. Early intervention, initiated soon after receiving an autism diagnosis, has been shown to have significant benefits in improving developmental outcomes and enhancing the quality of life for individuals on the autism spectrum.
Understanding the feedback provided after an autism assessment and following through with the recommended intervention and support services are essential steps in supporting the individual’s journey.
Complex and Time-Intensive Process
The autism assessment journey is a complex and time-intensive process that involves various professionals and evaluation methods. The assessment team typically includes professionals such as developmental pediatricians, child psychologists, child psychiatrists, speech-language pathologists, and occupational therapists. These professionals work together to assess the child’s behaviors, communication skills, cognitive abilities, and social interactions to determine if they meet the criteria for an autism diagnosis.
The assessment process itself is multifaceted, involving interviews with the child (if verbal), parents, and teachers. Standardized tests, observations, and questionnaires are also utilized to gather information about the child’s behavior and development. The data collected from these assessments is carefully analyzed to form a comprehensive evaluation of the child’s strengths and challenges.
Due to the complexity and thoroughness of the assessment process, it may take considerable time to complete. Patience is essential during this period, as professionals need to ensure accurate and reliable results. It is important for parents and caregivers to remain engaged and actively participate throughout the assessment journey. They can seek support from professionals, connect with support groups, and educate themselves about the process to better advocate for their child.

The Role of Parents and Caregivers
Advocating for your child is a crucial aspect of the autism assessment process. As a parent or caregiver, you are the primary voice for your child, ensuring that their needs are heard and addressed. Here are some key ways you can advocate for your child during the assessment:
- Seeking an Evaluation: If you suspect your child may have autism, take the initiative to seek an evaluation from qualified professionals. It’s important to reach out to healthcare providers, educators, or specialists experienced in autism assessments.
- Sharing Concerns and Observations: Be proactive in sharing your concerns and observations about your child’s behavior, development, and challenges. Providing detailed information to the assessing professionals can assist them in gaining a comprehensive understanding of your child’s needs.
- Collaborating with Professionals: Collaborate with the professionals involved in the assessment process. Share relevant information about your child’s medical and developmental history, as well as any previous assessments or interventions. Actively engage in discussions and ask questions to ensure a clear understanding of the assessment process.
- Participating in Assessments: Depending on your child’s age and abilities, your participation may be required during the assessment. Your input through interviews and questionnaires can provide valuable insights into your child’s behavior and development.
Understanding the Assessment Process
To effectively support your child, it is important to have a clear understanding of the assessment process. While the specific methods and tools used may vary, the process typically involves the following steps:
- Medical and Developmental History: You will be asked to provide a detailed medical and developmental history of your child. This information helps in understanding your child’s background and any relevant factors that may impact the assessment.
- Direct Observation and Interviews: Assessors may conduct direct observations of your child’s behavior to gather firsthand information. Additionally, interviews with you and other caregivers, as well as teachers, may be conducted to gain different perspectives on your child’s behavior.
- Standardized Assessments: Standardized assessments, such as the Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule (ADOS) and the Autism Diagnostic Interview-Revised (ADI-R), are commonly used tools in autism assessments. These assessments help to evaluate your child’s specific strengths and challenges related to autism.
By actively participating in the assessment process and understanding its various components, parents and caregivers can contribute to a comprehensive evaluation of their child’s needs. This understanding will also assist in making informed decisions regarding interventions and support services after receiving an autism diagnosis.

