Genetic testing is a valuable tool that plays a significant role in unraveling the genetic mystery behind autism. By examining a person’s genes and chromosomes, genetic testing can provide insights into the potential genetic factors contributing to autism spectrum disorder (ASD). In this section, we will explore the types of genetic testing and the purpose each serves.
Types of Genetic Testing
There are three main types of genetic testing used in relation to autism:
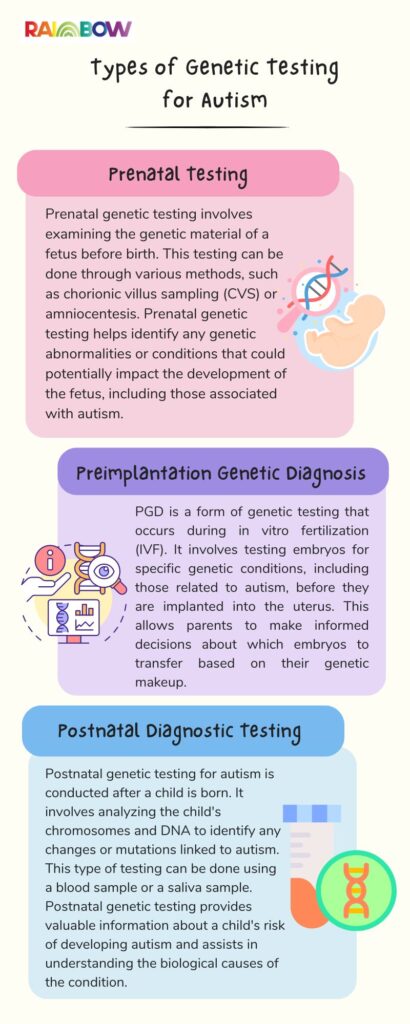
Purpose of Genetic Testing
Genetic testing for autism serves multiple purposes and offers potential benefits for individuals and families. Some of these include:
- Early Diagnosis: Genetic testing can contribute to the early diagnosis of autism. Early diagnosis is crucial as it allows for timely support and treatment, which can significantly impact a child’s development. Early intervention services, such as behavioral therapy, speech therapy, and occupational therapy, can be initiated to provide targeted support.
- Understanding Genetic Causes: Genetic testing provides insights into the genetic factors contributing to autism. It helps researchers and healthcare professionals better understand the biological mechanisms underlying the condition. This knowledge can lead to advancements in the field of autism research and potentially pave the way for more effective interventions and treatments.
- Informed Parental Decisions: Genetic testing assists families in making informed decisions regarding their child’s health and development. It provides information about a child’s risk of developing autism and can aid in family planning and reproductive decision-making.
It is important to note that while genetic testing for autism offers valuable information, it is not a definitive diagnostic tool. It provides insights into the genetic aspects of autism but does not provide a conclusive diagnosis on its own. It is recommended to consult with a healthcare provider to determine if genetic testing is appropriate for your family.
Genetic Testing for Autism
Genetic testing plays a vital role in unraveling the complex genetic factors associated with autism. By examining a child’s chromosomes and DNA, genetic testing can help identify changes or mutations linked to autism. In this section, we will explore the testing methods used, the benefits it offers, as well as its limitations.
Testing Methods
Genetic testing for autism can be conducted using a blood sample or a saliva sample. These samples are analyzed in specialized laboratories to identify changes in specific genes associated with autism. It’s important to note that genetic testing does not definitively diagnose autism, but rather provides information about a child’s risk of developing the condition.
Limitations of Genetic Testing
While genetic testing for autism is valuable in providing information about a child’s risk of developing the disorder, it does have limitations. It’s essential to recognize that changes in specific genes associated with autism can increase the risk of developing the condition, but they do not guarantee that the child will have autism. The interplay of genetics with environmental factors is complex, and the presence of genetic changes does not always result in autism.
Genetic testing is just one piece of the diagnostic puzzle, and a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare provider is necessary to make an accurate diagnosis. Genetic testing should be viewed as a tool to aid in understanding the child’s risk for autism, rather than a standalone diagnostic tool.
Controversies Surrounding Genetic Testing
Genetic testing for autism is a complex and multifaceted topic that can elicit various controversies. While it plays a significant role in unraveling the genetic mysteries associated with autism, it also raises ethical concerns, legal implications, and social issues.
Ethical Concerns
Ethical concerns arise when considering the potential implications of genetic testing for autism. One of the primary concerns is the possibility of discrimination based on genetic information. Individuals who test positive for certain genetic markers associated with autism may face discrimination in areas such as employment, insurance coverage, and educational opportunities. This raises ethical questions about the privacy and confidentiality of genetic information.
Moreover, genetic testing for autism may present psychological burdens for parents and families. The results of genetic testing can bring uncertainty, anxiety, and emotional distress, particularly when there are no definitive treatment options available. It is essential for healthcare providers to offer proper counseling and support to individuals and families undergoing genetic testing to address these ethical concerns.
Legal Implications
The field of genetic testing for autism also raises legal implications. Legislation regarding the protection of genetic information varies across different jurisdictions. Laws and regulations related to privacy, discrimination, and access to genetic services can significantly impact the utilization and availability of genetic testing for autism.
Legal frameworks must safeguard individuals and families from potential discrimination based on genetic information. It is crucial to advocate for laws that protect the rights and privacy of individuals undergoing genetic testing, ensuring equal access to services and preventing discrimination based on genetic predispositions.
Social Issues
Social issues surround genetic testing for autism as well. Unequal access to genetic services is a concern, as individuals from disadvantaged backgrounds may face barriers in obtaining genetic testing due to financial constraints, lack of awareness, or limited access to healthcare resources. This inequality can lead to disparities in diagnosis and treatment options.
Additionally, the interpretation of genetic testing results can be complex and requires specialized knowledge. Ensuring that healthcare professionals and genetic counselors are adequately trained to provide accurate and comprehensive information to individuals and families is essential. This helps to bridge the gap between scientific advancements and public understanding, enabling informed decision-making regarding genetic testing for autism.

Risks Associated with Genetic Testing
While genetic testing for autism offers numerous benefits, it is important to be aware of the potential risks and limitations associated with this type of testing. Understanding these risks can help individuals make informed decisions and manage their expectations. Two significant risks to consider are false results and the importance of consultation with a healthcare provider.
False Results
One of the risks associated with genetic testing for autism is the possibility of false results. False positive results occur when the test indicates the presence of a genetic variant associated with autism, but the individual does not actually have the condition. On the other hand, false negative results occur when the test fails to detect a genetic variant associated with autism, even though the individual may have the condition.
It is crucial to understand that genetic testing for autism cannot definitively diagnose autism. It provides information about a child’s risk of developing the condition based on identified genetic changes or mutations. It is recommended to consult a healthcare provider to discuss the interpretation of genetic test results and understand their implications fully ABA Therapy Services should be considered as part of a comprehensive approach to supporting individuals with autism.
Conclusion
Before undergoing genetic testing for autism, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider who specializes in genetics or autism. A healthcare provider can explain the available testing methods, the possible outcomes, and the limitations of genetic testing. They can also help individuals understand the potential benefits and risks specific to their situation, as each case may vary.
Healthcare providers can guide individuals through the genetic testing process, explain the significance of the results, and provide appropriate support and resources.
It is essential to remember that genetic testing is just one tool in understanding the potential risk of autism. It does not provide a definitive diagnosis, but rather contributes to a comprehensive assessment of the risk factors associated with autism.

